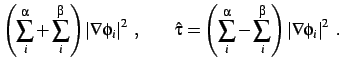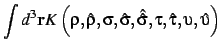Next: 17.1.1 S: Slater-Dirac exchange
Up: 17 THE DENSITY FUNCTIONAL
Previous: 17 THE DENSITY FUNCTIONAL
In the following,
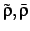 are the
are the  spin densities;
the total and spin densities are
spin densities;
the total and spin densities are
the gradients of the density enter through
Additionally, the kinetic energy density for a set of
(Kohn-Sham) orbitals generating the density can be introduced through
All of the available functionals are of the general form
Subsections
P.J. Knowles and H.-J. Werner
molpro-support@tc.bham.ac.uk
Mar 8, 2000