This submodule is the driver for geometry optimizations, although we
note that the
*WALK module contains another second-order
geometry optimization driver. The
*OPTIMIZE module contains both first and second-order methods
for locating minima and transition states
(geometry optimization). Most of the Hessian
updating schemes were taken from
ref.[108] and [23]. The implementation of
redundant internal coordinates
follows the work of Peng et al. [109]. In
addition to this, several keywords for VRML visualization are
included [110].
-
.1STORD
- Use default first-order method.
This means that the BFGS update will
be used, and that the optimization is carried out in redundant internal
coordinates. Same effect as the
combination of the two keywords
.BFGS and
.REDINT. Since the
.BFGS method ensures a positive definite Hessian, the
.BOFILL optimization method is used by default in case of
searches for transition states.
-
.2NDORD
- Use default second-order method.
Molecular Hessians will be calculated at every
geometry. The level-shifted Newton method and
Cartesian coordinates are used. Identical
to specifying the keywords
.NEWTON and
.CARTES.
-
.BAKER
- Activates the convergence criteria of Baker [34]. The minimum
is then said to be found when the largest element of the gradient
vector (in Cartesian or redundant internal coordinates) falls below
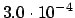 and either the energy change from the last
iteration is less than
and either the energy change from the last
iteration is less than
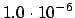 or the largest element of
the predicted step vector is less
or the largest element of
the predicted step vector is less
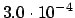 .
.
-
.BFGS
- Specifies the use of a first-order method
with the Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno (BFGS)
update
formula for optimization. This is the
preferred first-order method for minimizations, as this update is able
to maintain a positive definite Hessian. Note that this also makes it
unsuitable for transitions state optimization (where one negative
eigenvalue is sought).
-
.BFGSR1
- Use a linear combination of the BFGS and the symmetric rank one
updating schemes in the same fashion as Bofill's update. Only suitable
for minimizations.
-
.BOFILL
- Bofill's update[35]
is the default updating scheme for
transition state optimizations. It's a linear combination of the
symmetric rank one and the PSB updating schemes, automatically giving
more weight to PSB whenever the rank one potentially is numerically
unstable.
-
.CARTES
- Indicates that Cartesian coordinates
should be used in the optimization. This is the default for
second-order methods.
-
.CMBMOD
- Uses a combination of the BFGS update and the model Hessian (diagonal
in redundant internal coordinates). The two have equal weight in the
first iteration of the geometry optimization, then for each subsequent
iteration the weight of the model Hessian is halved. Only suitable for
minimizations.
-
.CONDIT
READ (LUCMD,*) ICONDI
Set the number of convergence criteria
that should be fulfilled before
convergence occurs. There are three different convergence thresholds,
one for the energy, one for the gradient
norm and one for the step
norm. The possible values for this variable is
therefore between 1 and
3. Default is 2. The three convergence thresholds can be adjusted with
the keywords
.ENERGY,
.GRADIE and
.STEP T.
-
.CONSTRAINT
READ (LUCMD, *) NCON
DO I = 1, NCON
READ(LUCMD,*) ICON
ICNSTR(ICON) = 1
END DO
Request a constrained geometry optimization. Only works when using
redundant internal coordinates. The number of primitive coordinates
that should be frozen has to be specified (NCON), then a list
follows with the individual coordinate numbers. The coordinate numbers
can be found by first running DALTON with the
.FINDRE
keyword. Any number of bonds, angles and dihedral angles may be
frozen. NOTE: Symmetry takes precedence over constraints, if you
e.g. want to freeze just one of several symmetric bonds, symmetry
must be lowered or switched off.
-
.DELINT
- Use delocalized internal coordinates.
These are built up as
non-redundant linear combinations of the redundant internal
coordinates. Performance is more or less the same as for the redundant
internals, but the transformation of displacements (step) is slightly
less stable.
-
.DFP
- Specifies that a first-order method with the
Davidon-Fletcher-Powell (DFP) update
formula should be used for optimization. May be used for both
minimizations and transition state optimizations.
-
.DISPLA
READ (LUCMD,*) DISPLA
Read one more line containing the norm of the displacement vector to
be used during numerical evaluation of the molecular gradient, as is
needed when doing geometry optimizations with CI or MP2 wave
functions. Default is
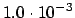 a.u.
a.u.
-
.ENERGY
READ(LUCMD,*) THRERG
Set the convergence threshold for the energy. This is one of the three
convergence thresholds (the keywords
.GRADIE and
.STEP T
control the other two). Default value is the maximum of
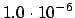 and two times the threshold for the wave function gradient.
and two times the threshold for the wave function gradient.
-
.FINDRE
- Determines the redundant internal coordinate system then quits without
doing an actual calculation. Useful for setting up constrained
geometry optimizations, where the numbers of individual primitive
internal coordinates are needed.
-
.GDIIS
- Use the Geometrical DIIS[111]
algorithm to control the
step. Works in much the same way as DIIS for wave functions. However,
the rational function and level-shifted Newton methods are generally
more robust and more efficient. Can only be used for minimizations.
-
.GEOANA
- Enables an analysis of the molecular geometry in terms of bond lengths
and bond angles at each new geometry predicted during the optimization
procedure.
-
.GRADIE
READ(LUCMD,*) THRGRD
Set the convergence threshold for the gradient norm. This is one of
the three convergence thresholds (the keywords
.ENERGY and
.STEP T control the other two). Default value is the maximum of
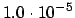 and two times the threshold for the wave function
gradient.
and two times the threshold for the wave function
gradient.
-
.GRDINI
- Specifies that the Hessian should be
reinitialized every time the norm
of the gradient is larger than norm of the gradient two iterations
earlier. This keyword should only be used when it's difficult to
obtain a good approximation to the Hessian during optimization. Only
applies to first-order methods.
-
.HELLMA
- Use gradients and Hessians calculated using the Hellmann-Feynman
approximation. Currently not working properly
-
.HESFIL
- Specifies that the initial Hessian
should be
read from the file
DALTON.HES. This applies to first-order
methods, and the Hessian in the file must have the correct
dimensions. This option overrides other options for the initial
Hessian.
Each time a Hessian is calculated or updated,
it's written to this file (in Cartesian coordinates). If an
optimization is interrupted, it can be restarted with the
last geometry and the Hessian in DALTON.HES, minimizing the
loss of information. Another useful possibility, is to transfer
the Hessian from a calculation on the same molecule with another
(smaller) basis and/or a cheaper wave function. Finally, one can go in
and edit the file directly to set up a specific force field.
-
.INIMOD
-
Use a simple model Hessian [33] diagonal in redundant
internal coordinates as the initial Hessian. All diagonal elements are
determined based on an extremely simplified molecular mechanics model,
yet this model provides Hessians that are good starting points for
most systems, thus avoiding any calculation of the exact Hessian. This
is the default for first-order methods.
-
.INIRED
- Specifies that the initial Hessian
should be diagonal in redundant internal coordinates. The different diagonal
elements are set equal to 0.5 for bonds, 0.2 for angles and 0.1 for
dihedral angles, unless
.INITEV has been specified. If the
optimization is run in Cartesian coordinates, the diagonal internal
Hessian is transformed to Cartesians. Only applies to first-order
methods.
-
.INITEV
READ(LUCMD,*) EVLINI
The default initial Hessian for first-order
minimizations is the
identity matrix when Cartesian coordinates are used, and a diagonal
matrix when redundant internal coordinates are used. If
.INITEV
is used, all the diagonal elements (and therefore the eigenvalues) are
set equal to the value EVLINI. This option only has effect when
first-order methods are used and
.INITHE and
.HESFIL are
non-present.
-
.INITHE
-
Specifies that the initial Hessian should be
calculated (analytical Hessian), thus yielding a first step that is
identical to that of second-order methods. This provides an excellent starting
point for first-order methods, but should only be used when the
Hessian can be calculated within a reasonable amount of time. It has only
effect for first-order methods and overrides the keywords
.INITEV and
.INIRED. It has no effect when
.HESFIL has
been specified.
-
.LINE S
- Turns on line searching,
using a quartic polynomial. By default this
is turned off, as there seems to be no gain in efficiency. Can only be
used for minimizations.
-
.M-BFGS
- A list of old geometries and gradients are kept. At each new point,
displacements and gradient difference for the last few steps are
calculated, and all of these are then used to sequentially update the
Hessian, the most weight being given to the last displacement and
gradient difference. Each update is done using the BFGS formula, and
it's thus only suitable for minimizations. Only applies to first-order
methods.
-
.M-PSB
- This identical to
.M-BFGS, except the PSB formula is used for the
updating. Only applies to first-order methods, but it can be used for both minimizations and saddle
point optimizations.
-
.MAX IT
READ(LUCMD,*) ITRMAX
Read the maximum number of geometry iterations.
Default value is 25.
-
.MAX RE
READ(LUCMD,*) MAXREJ
Read maximum number of rejected steps
in each iterations, default is 3.
-
.MODE
READ(LUCMD,*) NSPMOD
Only has effect when doing saddle point optimizations.
Determines which Hessian eigenmode should be maximized (inverted in the image
method). By default this is the mode corresponding to the lowest
eigenvalue, i.e. mode 1. If an optimization does not end up at
the correct transition state, it may be worthwhile following other modes
(only the lower ones are usually interesting).
-
.MODHES
- Determine a new model Hessian (see
.INIMOD)
at every geometry without doing any updating. The model is thus used
in much the same manner as an exact Hessian, though it is obviously
only a relatively crude approximation to the analytical Hessian.
-
.NEWTON
- Specifies that a second-order Newton method should be used for
optimization--that is, the analytical Hessian will be calculated at
every geometry. By default the level-shifted trust region method will
be used, but it is possible to override this by using one of the two
keywords
.RF or
.GDIIS.
-
.NOAUX
- Only has effect when using redundant internal coordinates. The default
for minimizations is to add auxiliary bonds between atoms that are up
to two and half times further apart then regular (chemical)
bonds. This increases the redundancy of the coordinate system, but
usually speeds up the geometry optimization slightly.
.NOAUX
turns this off. For saddle point optimizations and constrained
geometry optimization this is off by default (cannot be switched on).
-
.NOBREA
- Disables breaking of symmetry.
The geometry will be optimized within the given symmetry, even if a non-zero Hessian
index is found. The default is to let the symmetry be broken until
a minimum is found with a Hessian index of
zero. This option only has effect when second-order methods are used.
-
.NODIHE
- Only has effect when using redundant internal coordinates. Removes all
coordinates that are dihedral angles, leaving only bonds and
angles. Not too useful, but may be used if one wants to limit the
number of internal coordinates. Constrained geometry optimizations can
sometimes benefit from having all dihedral angles removed (assuming no
dihedral angles needs to be frozen).
-
.NOTRUS
- Turns off the trust radius, so that a full Newton step
is taken in each iteration. This should be used with caution, as
global convergence is no longer guaranteed. If long steps are desired,
it is safer to adjust the initial trust radius and the limits for the
actual/predicted energy ratio.
-
.PREOPT
READ (LUCMD,*) NUMPRE
DO I = 1, NUMPRE
READ (LUCMD,*) PREBTX(I)
END DO
First we read the number of basis sets that should be
used for preoptimization, then we read those
basis set names as strings. These
sets will be used for optimization in the order they appear in the
input. One should therefore place the smaller basis at the
top. After the preoptimization, optimization is performed with the
basis specified in the molecule input file.
-
.PRINT
READ (LUCMD,*) IPRINT
Set print level for this module. Read one more line containing print
level. Default value is 0, any value higher than 12 gives debugging
level output.
-
.PSB
- Specifies that a first-order method with the
Powell-Symmetric-Broyden (PSB)
update formula should be used for optimization.
-
.RANKON
- Specifies that a first-order method with the rank one update
formula should be used for optimization. This updating is also
referred to as symmetric rank one (SR1) or Murtagh-Sargent (MS).
-
.REDINT
- Specifies that redundant internal coordinates
should be used in the optimization. This is the default for
first-order methods.
-
.REJINI
- Specifies that the Hessian should be
reinitialized after every
rejected step, as a rejected step
indicates that the Hessian models the
true potential surface poorly. Only applies to first-order
methods.
-
.REMOVE
READ (LUCMD, *) NREM
DO I = 1, NREM
READ(LUCMD,*) IREM
ICNSTR(IREM) = 2
END DO
Only has effect when using redundant internal coordinates.
Specifies internal coordinates that should be removed. The input is
identical to the one for
.CONSTRAINT, that is one has to specify
the number of coordinates that should be removed, then the number of
each of those internal coordinates. The coordinate numbers can first
be determined by running with
.FINDRE set.
Removing certain coordinates can sometimes be useful in speeding up
constrained geometry optimization, as certain coordinates sometimes
``struggle'' against the constraints. See also
.NODIHE.
-
.RF
- Use the rational function method [27] instead of
level-shifted Newton which is the default. The RF method is often
slightly faster than the level-shifted Newton, but also slightly less
robust.
For saddle point optimizations there's a special partitioned rational
function method (used automatically when both
.RF
and
.SADDLE are set). However, this method is both slower and
less stable than the default trust-region level-shifted image method
(which is the default).
-
.SADDLE
- Indicates that a saddle point optimization should be performed rather
than a minimization. The default method is to calculate the Hessian
analytically at the initial geometry, then update it using Bofill's
update. The optimization is performed in redundant internal
coordinates and using the trust-region level-shifted image method to
control the step. That is by default all the keywords
.INITHE,
.BOFILL and
.REDINT are already set, but this can of course
be overridden by specifying other keywords. If locating the desired
transition state is difficult, and provided analytical Hessians are
available, it may sometimes be necessary to use the
.NEWTON
keyword so that Hessians are calculated at every geometry.
-
.SCHLEG
- Specifies that a first-order method
with Schlegel's updating scheme
[112] should be used. This makes use of all previous
displacements and gradients, not just the last, to update the
Hessian.
-
.SP BAS
READ(LUCMD,*) SPBSTX
Read a string containing the name of a basis set. When the geometry
has converged, a single-point energy will be calculated using this
basis set.
-
.STABILIZE
READ(LUCMD,*) ISTBLZ
Tries to ``stabilize'' the predicted new molecular geometries (and
thus reduce the risk of symmetry breakings) by ignoring all numbers
appearing in the Cartesian coordinates of the atoms beyond digit
number ISTBLZ.
-
.STEEPD
- Specifies that the first-order steepest descent method should be
used. No update is done on the Hessian, so the optimization will be
guided by the gradient alone. The ``pure'' steepest descent method is
obtained when the Hessian is set equal to the identity matrix. Each
step will then be the negative of the gradient vector, and the
convergence towards the minimum will be extremely slow. However, this
option can be combined with other initial Hessians in Cartesian or
redundant internal coordinates, giving a method
where the main feature is the lack of Hessian updates (static
Hessian).
-
.STEP T
READ(LUCMD,*) THRSTP
Set the convergence threshold for the step
norm. This is one of the
three convergence thresholds (the keywords
.ENERGY and
.GRADIE control the other two). Default value is
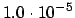 .
.
-
.SYMTHR
READ(LUCMD,*) THRSYM
Determines the gradient threshold for breaking of the
symmetry. That is, if the index of the
Hessian is non-zero when the gradient norm
drops below this value, the symmetry is broken to avoid unnecessary
iterations within the wrong symmetry. This option only applies to
second-order methods and when the
keyword
.NOBREA is not present. The default value of this
threshold is
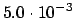 .
.
-
.TR FAC
READ(LUCMD,*) TRSTIN, TRSTDE
Read two factors that will be used for increasing and decreasing the
trust radius respectively. Default values are
1.2 and 0.7.
-
.TR LIM
READ(LUCMD,*) RTENBD, RTENGD, RTRJMN, RTRJMX
Read four limits for the ratio between the actual and predicted
energies. This ratio indicates how good the step is--that is, how
accurately the quadratic model describes the true energy
surface. If the ratio is below RTRJMN or above
RTRJMX, the step is rejected. With a ratio between
RTRJMN and RTENBD, the step is considered bad an the
trust radius decreased to less than the step
length. Ratios between RTENBD and RTENGD are
considered satisfactory, the trust radius is set equal to the norm
of the step. Finally ratios above RTENGD (but below
RTRJMX) indicate a good step, and the trust radius is given
a value larger than the step length. The amount the trust radius
is increased or decreased can be adjusted with
.TR FAC. The
default values of RTENBD, RTENGD, RTRJMN and
RTRJMX are 0.4, 0.8, -0.1 and 3.0 respectively.
-
.TRSTRG
- Specifies that the level-shifted trust region method should be used to
control the step. This is the default, so the keyword is actually
redundant at the moment. Alternative step control methods are
.RF
and
.GDIIS.
-
.TRUSTR
READ(LUCMD,*) TRSTRA
Set initial trust radius for calculation. This
will also be the
maximum step length for the first iteration. The trust radius is
updated after each iteration depending on the ratio between predicted
and actual energy change. The default trust radius is 0.5 a.u.
-
.VISUAL
- Specifies that the molecule should be
visualized,
writing a VRML file of the molecular geometry. No optimization
will be performed when this keyword is given. See also related
keywords
.VR-BON,
.VR-COR,
.VR-EIG and
.VR-VIB.
-
.VRML
- Specifies that the molecule should be
visualized. VRML files describing
both the initial and final geometry
will be written (as
initial.wrl and final.wrl). The file
final.wrl is updated in each iteration, so that it always
reflects the latest geometry. See also related keywords
.VR-BON,
.VR-COR,
.VR-EIG and
.VR-VIB.
-
.VR-BON
- Only has effect together with
.VRML or
.VISUAL. Specifies
that the VRML files should include bonds between nearby
atoms. The
bonds are drawn as grey cylinders, making it easier to see the
structure of the molecule. If
.VR-BON is omitted, only the
spheres representing the different atoms will be drawn.
-
.VR-COR
- Draws
 -,
-,  - and
- and  -axis in the VRML scenes with
geometries. Somewhat useful if one is struggling to build a reasonable
geometry by adjusting coordinates manually.
-axis in the VRML scenes with
geometries. Somewhat useful if one is struggling to build a reasonable
geometry by adjusting coordinates manually.
-
.VR-EIG
- Only has effect together with
.VRML or
.VISUAL.
Specifies that the eigenvectors of the molecule (that is the
eigenvectors of the Hessian, which differs from the normal modes as
they are not mass-scaled) should be visualized. These are written to
the files
eigv_###.wrl.
-
.VR-SYM
- Draws in all symmetry elements of the molecule as vectors (rotational
axes) and semi-transparent planes (mirror planes).
-
.VR-VIB
- Similar to
.VR-EIG, but more useful as it draws the actual normal
mode vectors (the mass-weighted eigenvectors). These are written to
the files
norm_###.wrl. Keyword only has effect when a
vibrational analysis has been requested.
![]() a.u.
a.u.
![]() and two times the threshold for the wave function gradient.
and two times the threshold for the wave function gradient.
![]() and two times the threshold for the wave function
gradient.
and two times the threshold for the wave function
gradient.
![]() .
.
![]() .
.